Google's Lumiere Shows More Momentum in AI Text-to-Video Innovation
Raising the bar in generative AI.
Google introduced its new Lumiere text-to-video foundation model research in a GitHub post this week. The model is not available for use or download but highlights Google’s innovation and the results of a new model design. It outputs videos of no more than 5 seconds in duration.
The company calls Lumiere “A Space-Time Diffusion Model for Realistic Video Generation.” Lumiere’s approach leverages parallel processing of the image and movement elements, while traditional approaches process the image and movement serially.
The new research landed shortly after the introduction of Stable Video Diffusion V2 in November, Pika Labs 1.0 in December, and ByteDance’s Magic Video V2 about ten days ago. According to Google’s announcement on GitHub:
We introduce Lumiere -- a text-to-video diffusion model designed for synthesizing videos that portray realistic, diverse and coherent motion -- a pivotal challenge in video synthesis. To this end, we introduce a Space-Time U-Net architecture that generates the entire temporal duration of the video at once, through a single pass in the model. This is in contrast to existing video models which synthesize distant keyframes followed by temporal super-resolution -- an approach that inherently makes global temporal consistency difficult to achieve. By deploying both spatial and (importantly) temporal down- and up-sampling and leveraging a pre-trained text-to-image diffusion model, our model learns to directly generate a full-frame-rate, low-resolution video by processing it in multiple space-time scales. We demonstrate state-of-the-art text-to-video generation results, and show that our design easily facilitates a wide range of content creation tasks and video editing applications, including image-to-video, video inpainting, and stylized generation.
Multiple Features
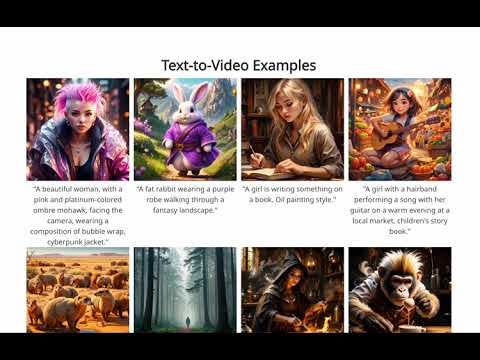
Lumiere is also versatile. Google researchers demonstrated text-to-video, image-to-video, stylized generation from a single reference image, cinematography, and video inpainting. Cinematography refers to the user identifying a segment of the image, and the model will animate only that region of the image. This is not an entirely new concept, but it is uncommon. Video in-painting enables the model to fill in the gaps if there is an obstruction.
Google provides examples for each of these output styles, and similar to other recently released models, the quality seems to be very high. That reaction is supported by the recent results from third-party testers.
Quality Comparison
Google Research conducted a quality comparison with outside testers. Other models evaluated include Imagen, Pika Labs, Zeroscope, Gen2, and Animate.
The results looks like a clear sweep of the market competition. Google outperformed existing, API-based AI services in every category. However, the model has its limits.
As for limitations, our method is not designed to generate videos that consist of multiple shots, or that involve transitions between scenes. Generating such content remains an open challenge for future research.
Most of the investment and positive generative ROI use cases will be driven by large language models (LLM) in 2024. However, that is a matter of scale. In terms of new-to-the-world innovation, text-to-video is likely a significant force for growth in 2024.